Secure Boot certificates are a hot topic these days, as several Microsoft Secure Boot certificates are set to expire in June 2026, potentially causing problems for Windows systems. It’s therefore crucial to update these certificates promptly.
There are several ways to update certificates, but in this blog post, I’d like to address the following use case, which involves thousands of non-domain-joined, MDM-managed Windows laptops using Omnissa Workspace ONE UEM. I am using the Registry key updates for Secure Boot.
First, you need to know which devices have Secure Boot enabled and whether they need an update.
To determine this, first create several Sensors in UEM and then use Omnissa Intelligence to read the sensors and create reports or dashboards.
Secure Boot Enable:
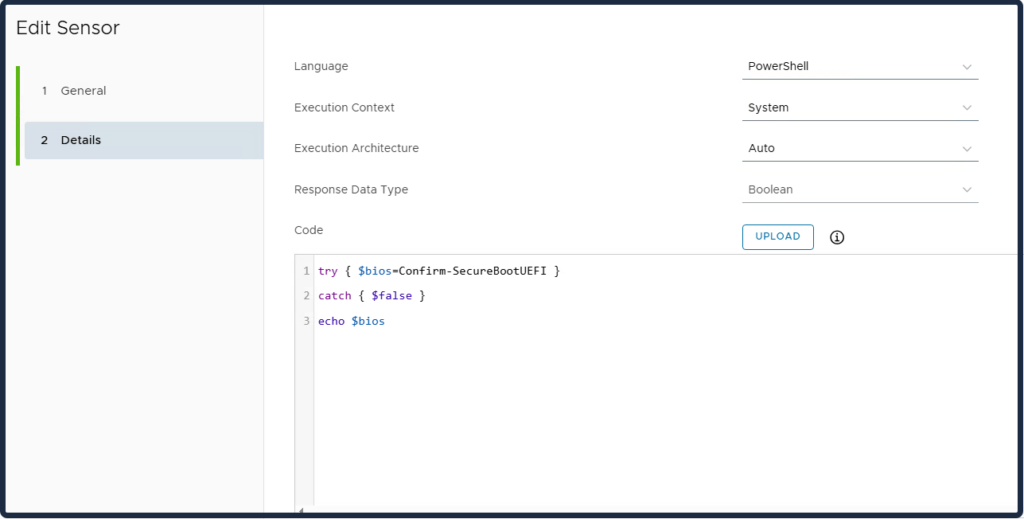
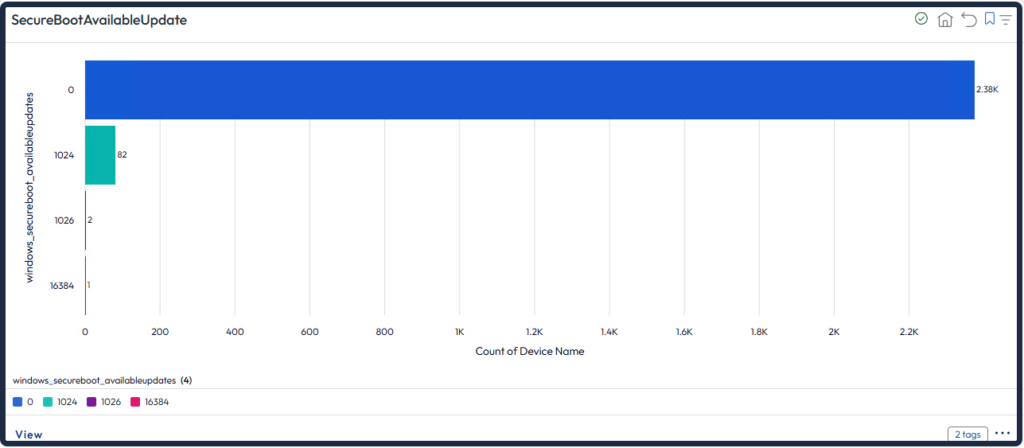
AvailableUpdates:
- 0 or not set – No Secure Boot key update are performed.
- 0x5944 – Deploy all needed certificates and update to the PCA2023 signed boot manager
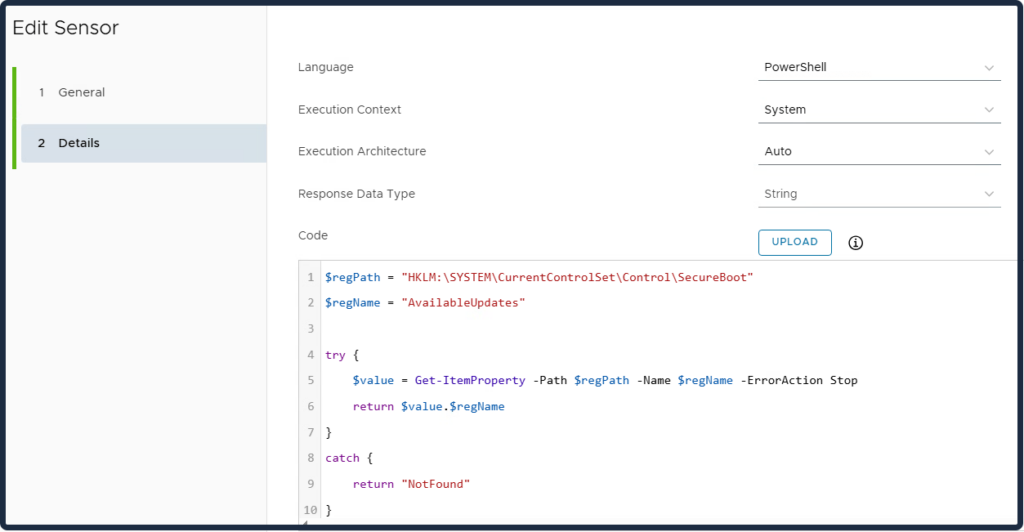
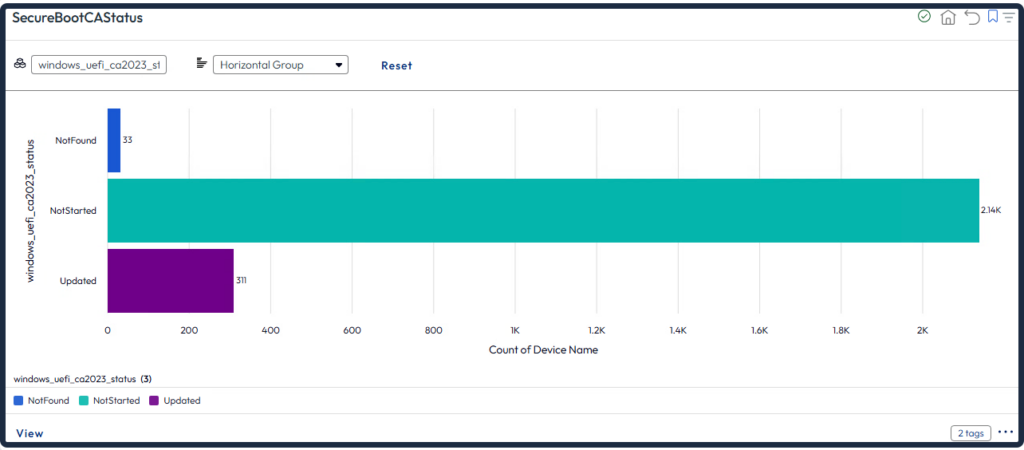
UEFICA2023Status:
- NotStarted: The update has not yet run.
- InProgress: The update is actively in progress.
- Updated: The update has completed successfully.
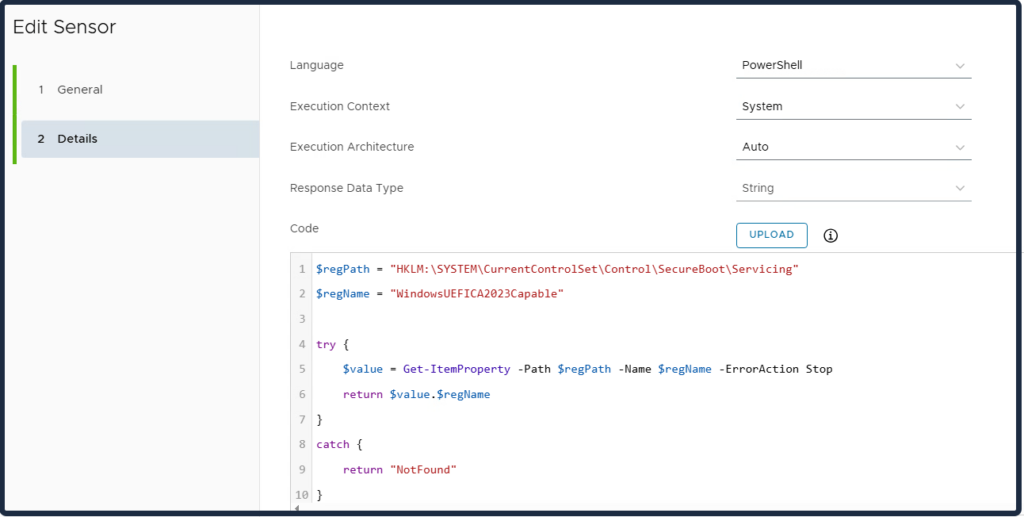
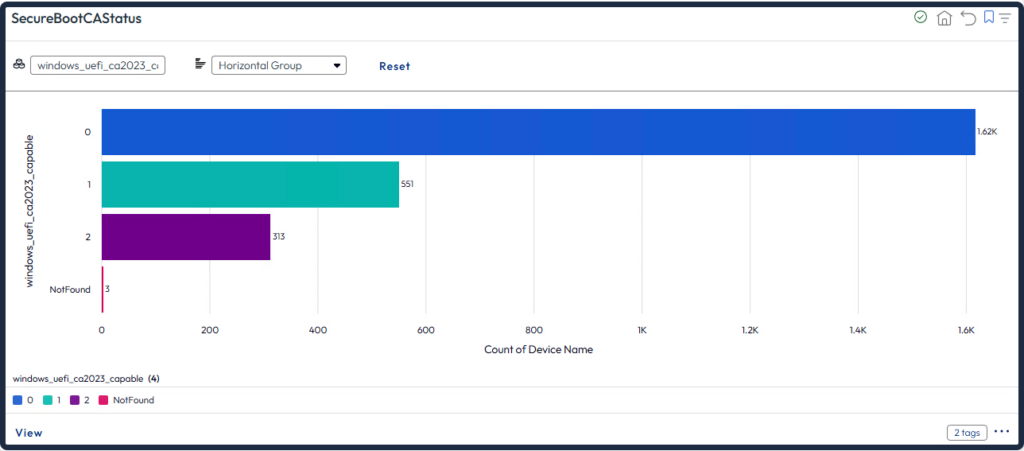
WindowsUEFICA2023Capable:
- 0 – or key does not exist – “Windows UEFI CA 2023” certificate is not in the DB
- 1 – “Windows UEFI CA 2023” certificate is in the DB
- 2 – “Windows UEFI CA 2023” certificate is in the DB and the system is starting from the 2023 signed boot manager
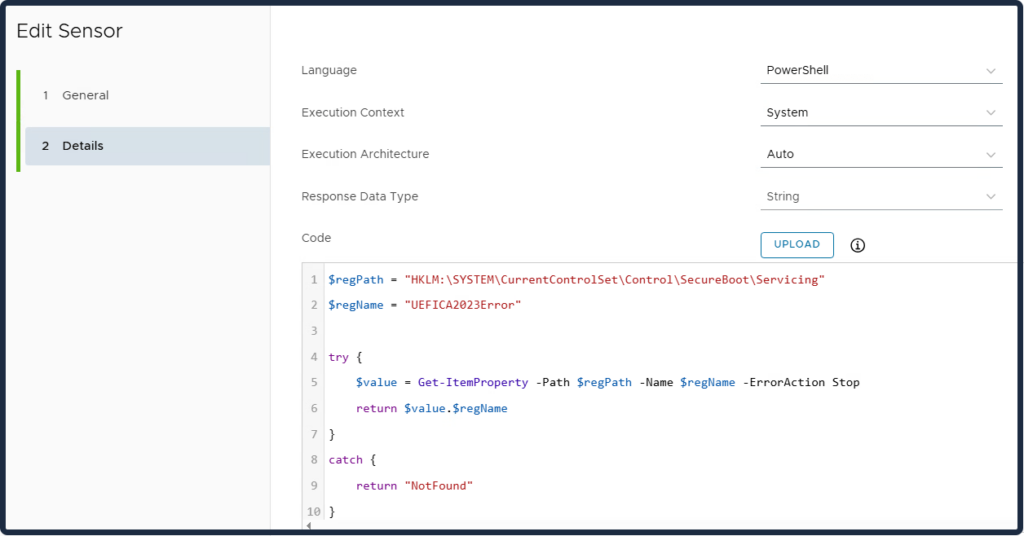
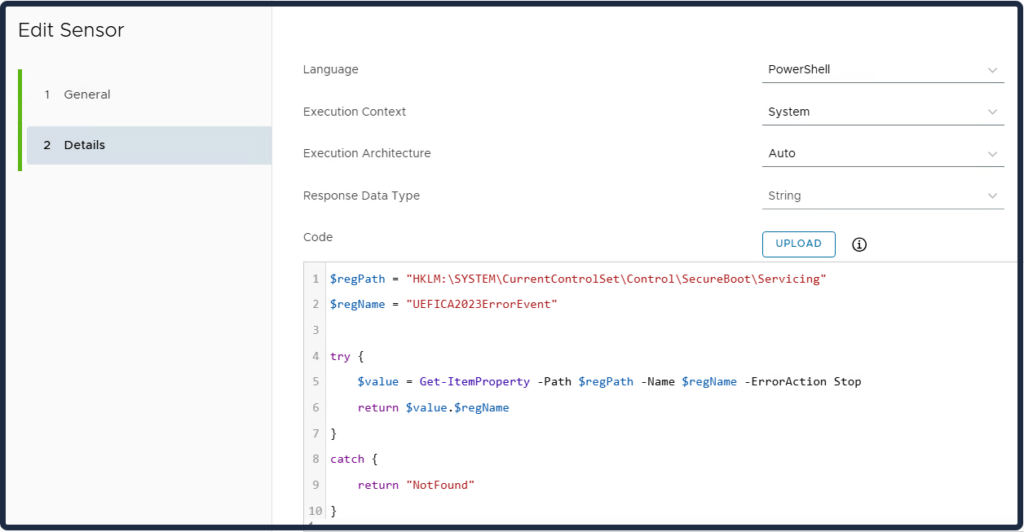
These two sensors are used for troubleshooting.
UEFICA2023Error and UEFICA2023ErrorEvent:
Error code (if any).
This value remains 0 on success. If the update process encounters a fault, UEFICA2023Error is set to a non-zero error code corresponding to the first error encountered. An error here implies the Secure Boot update did not fully succeed and may require investigation or remediation on that device.
This Sensor contains all the previous sensors to see all the information on a device at once.
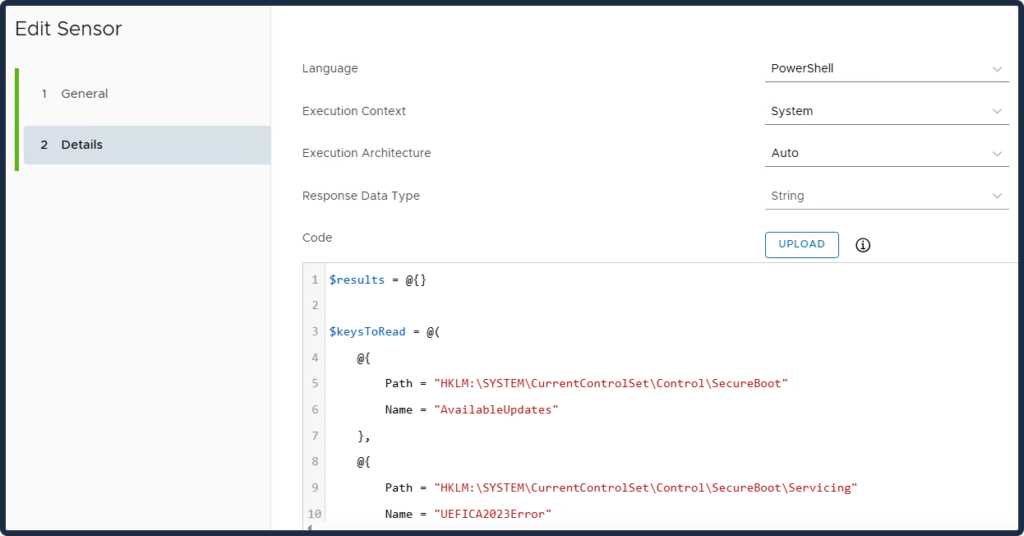
$results = @{}
$keysToRead = @(
@{
Path = "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecureBoot"
Name = "AvailableUpdates"
},
@{
Path = "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecureBoot\Servicing"
Name = "UEFICA2023Error"
},
@{
Path = "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecureBoot\Servicing"
Name = "UEFICA2023ErrorEvent"
},
@{
Path = "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecureBoot\Servicing"
Name = "UEFICA2023Status"
},
@{
Path = "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecureBoot\Servicing"
Name = "WindowsUEFICA2023Capable"
}
)
foreach ($key in $keysToRead) {
$fullKey = "$($key.Path)\$($key.Name)"
try {
$value = Get-ItemProperty -Path $key.Path -Name $key.Name -ErrorAction Stop
$results[$fullKey] = $value.$($key.Name)
}
catch {
$results[$fullKey] = "NotFound"
}
}
return ($results | ConvertTo-Json -Compress)Now that you’ve created all the Sensors, you can move on to Omnissa Intelligence to use reports and dashboards to gather all the information about Windows devices related to Secure Boot.

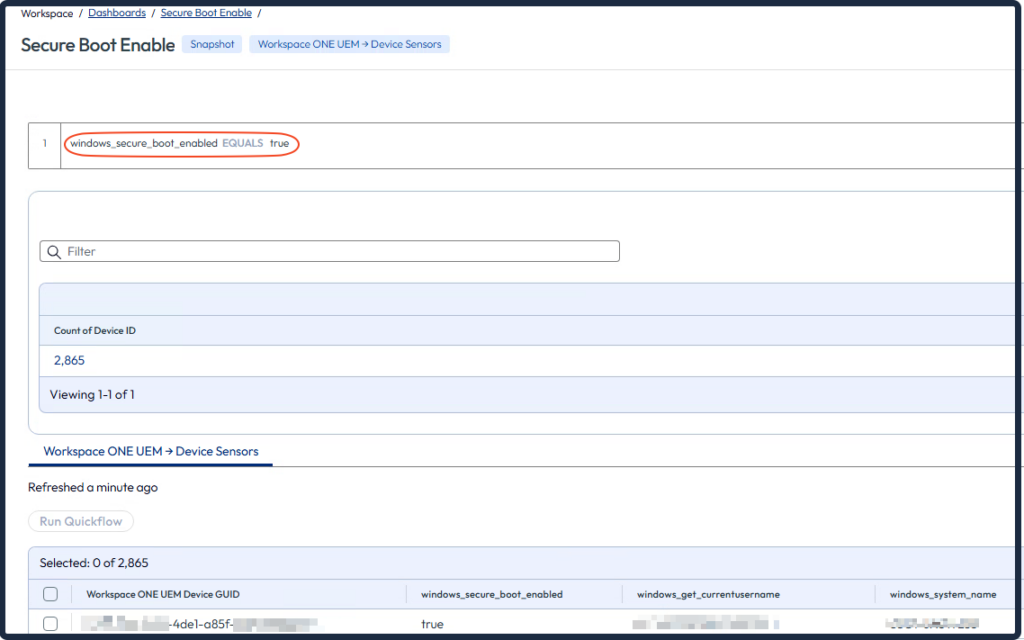
Create a dashboard to see which devices have Secure Boot enabled. Also see the user names, computer names, and manufacturer.
Create a dashboard to see the deployment status indicator.
Create a dashboard to see the Available Updates. Controls which Secure Boot update actions to perform on the device.
Create a dashboard to see the WindowsUEFICA2023Capable.
This registry key is intended for limited deployment scenarios and is not recommended for general use. For most cases, use the UEFICA2023Status registry key instead.
Now that you have all the information, you can create a workflow to update devices.
First, create a script in UEM.
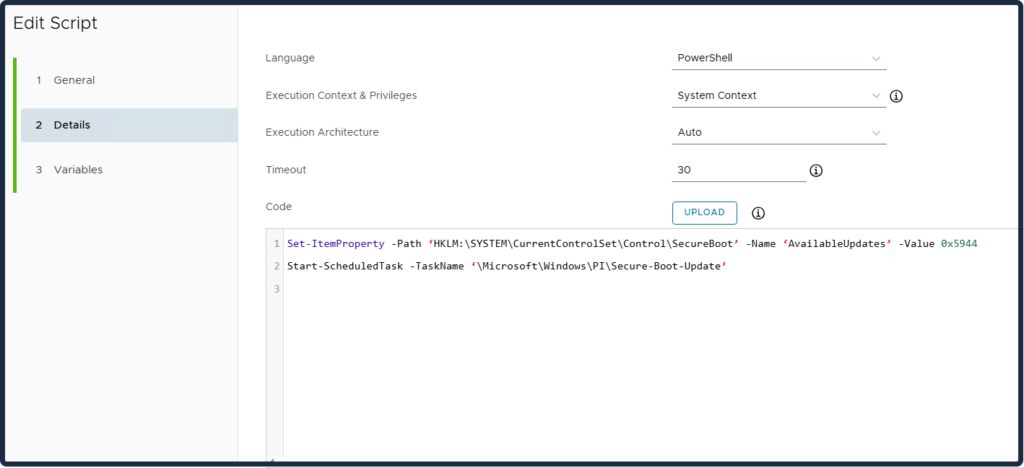
Then proceed to create Workflow via Orchestration.
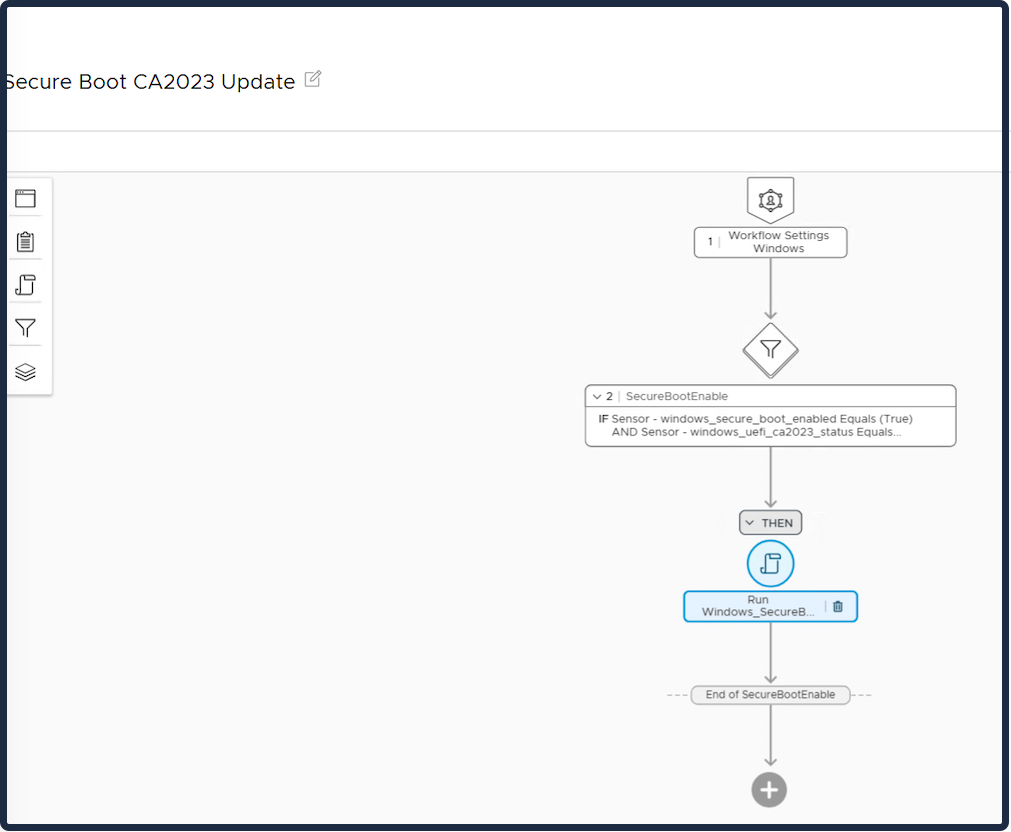
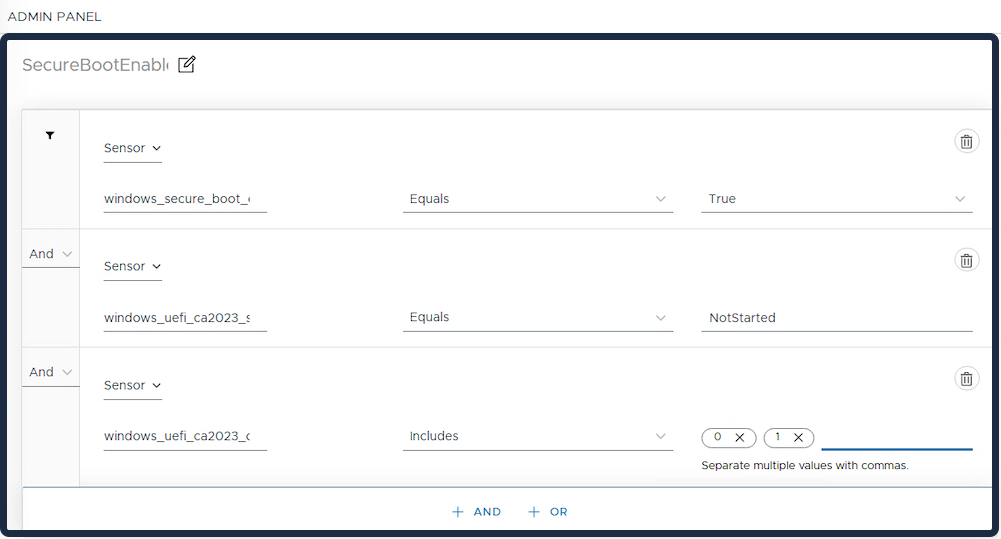
Conditions:
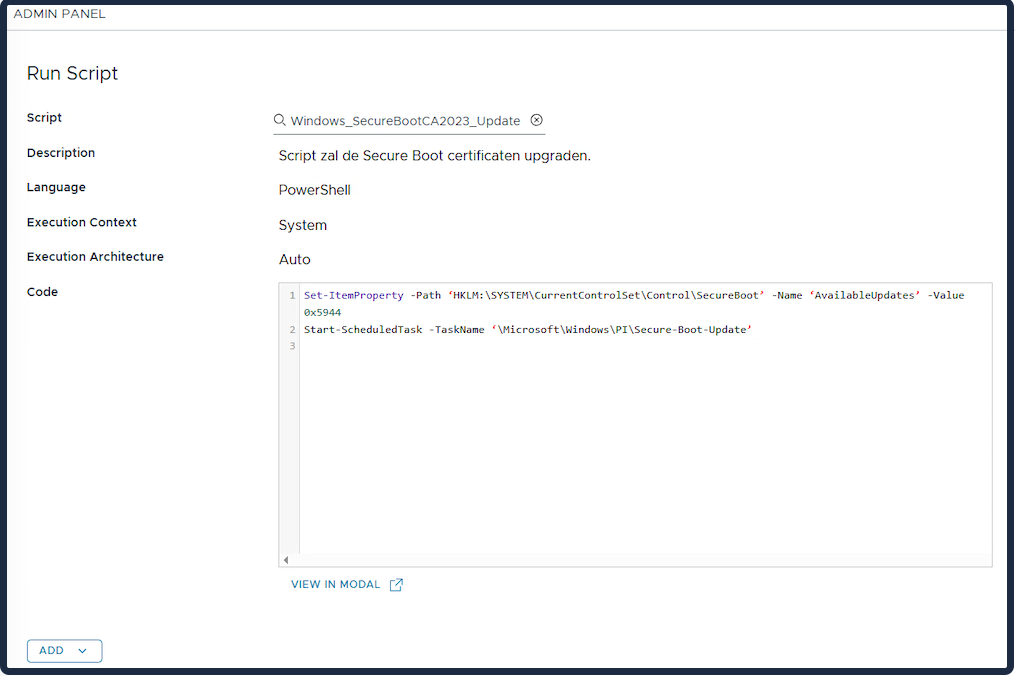
Run Script:
After the machine restarts, it will be updated. You can force the reboot or leave it until the user has restarted the machine. Sometimes it takes a while for the machine status to show “Updated”!
First, test a small number of Windows machines before attempting to update the entire environment!!!
Depending on the device manufacturer and model, some machines may have issues updating. In that case, you’ll need to contact the manufacturer for assistance, and you may need to update via OEM updates.
Microsoft is working on implementing the Secure Boot Certificate update via Windows Update as well.
